Cell Membrane
Definition: Very thin membrane surrounding the cell
L.M: -Invisible as it is very thin [8-10 nm] -But can be stained by PAS or Ag
E.M: Trilamellar membrane [Appears as 2 dark parallel lines, separated by light one]
Molecular structure of cell membrane: >> 1-Lipid Component [30%]
a-Phospholipid molecules
Arranged in 2 layers (bilipid layer)
Each molecule has a head & tail
b-Cholesterol molecules
-Protein Component [60%]
Integral protein [Channel or carrier protein]
Peripheral protein
Carbohydrate Component [10%]: -They are Polysaccharides. -Either attached to protein >> Glycoprotein or to lipid >> Glycolipid -Glycolipid + Glycoprotein >> Cell coat or [Glycocalyx]
Functions of Cell Membrane >> 1-Passive diffusion (for gases, water & ions) according to concentration gradient >> 2-Facilitated diffusion (with carrier): for glucose and amino acids. >> 3-Active transport (needs energy): e.g. Na+-K + pump. >> 4-Selective permeability (by receptors in cell coat): Allows entry of certain substances >> 5-Phagocytosis: Engulfment of solid materials >> 6-Pinocytosis: Engulfment of liquid materials >> 7-Exocytosis: Extrusion of substances outside the cell >> 8-Functions of cell coat: a-Mechanical protection of the cell b-Cell immunity & allergy
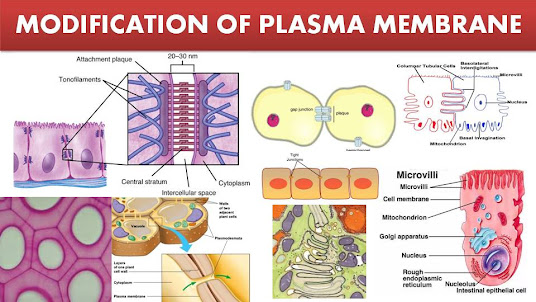
Modifications in Cell Membrane
Formation of microvilli → Increased surface area e.g: Absorptive cells in small intestine >> Formation of cilia → Move particles above cell membrane e.g: Removal of dust from inspired air in respiratory passages >> Formation of flagella → Helps movement e.g: Tails of sperms


No comments:
Post a Comment