Mitochondria
Definition: Power house of the cell [Responsible for cell respiration & energy production] Number: Numerous in active cells >> -Liver cells [contain up to 2000/cell] >>-Cardiac muscle >>-Kidney tubules
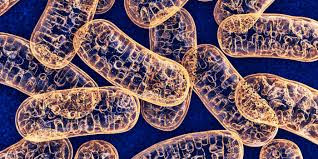
L.M: >>-Granules, rods or filaments. >>-Need special stains: Stains black with iron hematoxylin, stains green with Janus
E.M: >>-Round or oval vesicles >>-Covered with double membranes separated by inter >>-membranous space >>-Outer membrane is smooth >>-Inner membrane form folds [called cristae] >>-Matrix fills the internal cavity, contains: Lipid, Protein, Carbohydrate, Ca, Mg, DNA, RNA & Oxidative enzymes
Functions: >>1-Cell respiration [Power House]: Contain oxidative enzymes produce energy [ATP] through Krebs cycle. 50% of energy is stored as ATP 50% is dissipated as heat to keep normal body temperature >>2-Form their own proteins & can divide, as they contain DNA & RNA.
Role of Mitochondria in Apoptosis [Cell suicide] On exposure of the living cell to stress [Hypoxia, heat, viruses, DNA damage,…..], Mitochondria release Cytochrome C protein from inner membrane Activation of proteases enzymes in cytoplasm Apoptosis


No comments:
Post a Comment